The Healdsburg Regional Library is offering students a unique way to show their gratitude, and it couldn’t come at a more opportune time.
Wildfires that raged through Sonoma County and Napa Valley, Calif. in October left many in the area scrambling for safety as flames devoured their homes and belongings, but the library’s new Gratitude Tree is helping some to cope with the destruction, The Healdsburg Tribune reports.
Many Healdsburg residents were lucky enough to avoid the fires, Healdsburg librarian Charity Anderson said, but children in local schools haven’t escaped the reality that’s left friends and families in dire straits.
“The tree is exactly what it sounds like,” Anderson told the news site. “It invites people in the community to say what they’re grateful for and creates a beautiful art piece.”
“This is a good way for children to say what they’re grateful for, which is really important after the fires,” she said.
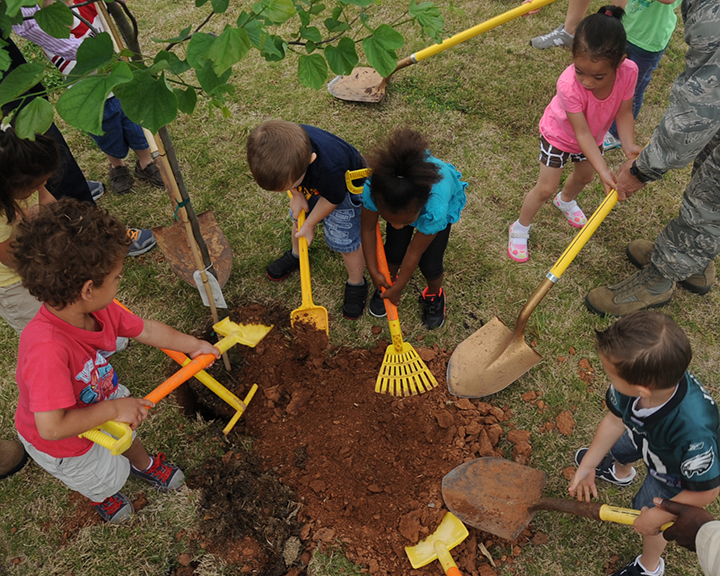
The idea for the Gratitude Tree started this summer, well before several fires scorched nearly 200,000 acres, consuming roughly 8,400 structures and killing dozens of people. Four children’s librarians from around the county came up with the low commitment idea to engage children for Gratitude Month in November using a tree, with paper leaves kids can use to write what they’re thankful for and hang from its branches.
At the Healdsburg library, officials unveiled the tree, which sits near the children’s area earlier this month, and it’s already filling in with leaves expressing thanks “for the first responders of Sonoma County,” “friends and family,” and other hopeful messages.
The Tribune notes that the National Child Traumatic Stress Network (NCTSN) emphasizes how wildfires often leave children with fear, worry, distress, and anxiety. The damage, both physical and emotional, stems from concerns about loved ones, separation from their families, and can lead to behavior problems, as well as problems sleeping or eating.
“Even in the most difficult situations, it is important to identify some positive aspect and to stay hopeful for the future,” the NCTSN advises. “A positive and optimistic outlook helps children see the good things in the world around them. This outlook can be one way to help them through even the most challenging times.”
Robert H. Frank also observed the intersection of gratitude and behavior in The Hedgehog Review, a publication of the Institute for Advanced Studies in Culture at the University of Virginia.
Frank pointed to the “large body of research by academic psychologists who have studied how the emotion of gratitude affects people’s behavior.”
“The general finding is that gratitude makes people not only happier and healthier, but also more generous toward others,” he wrote.
In other words, gratitude is infectious, particularly in folks who acknowledge that their good fortune isn’t entirely their own making.
“Interesting enough, gratitude is often stronger in people who believe that they have been lucky rather than in those who believe that success is solely due to their own efforts,” Frank wrote. “Subjects who’d been asked to recall a good event and come up with external causes—many of whom mentioned luck explicitly, or cited factors like supportive spouses, thoughtful teachers, and financial aid—gave more than 25 percent larger donations than those who’d been asked to offer internal causes to explain the good event.”
The fires in California have undoubtedly left many in the Napa Valley region grateful to be alive, and many surely recognize that prevailing winds, an act of God, or some form of luck played a role.
The Healdsburg Gratitude Tree provides an opportunity for local students to reflect on that reality, and share their gratitude for avoiding the terrible fate that befell their neighbors.
Anderson told the Tribune that’s something worth celebrating, and she now plans to keep the Gratitude Tree up through the end of the year to continue to spread the message of hope.
“Maybe we’ll even put Christmas lights on it,” she said.
Lessons from the Jubilee Centre can help students practice the virtue of gratitude in the classroom.